Every day, modern CPUs do millions of computations and procedures. Any phone, laptop, streaming device, bespoke gaming setup, you name it, they are the lifeblood. Although they always continue operating if the components around them are well-maintained. They can endure a very long period.
One of a computer’s most dependable parts is the CPU. The CPU will only often malfunction if one of its important parts, such as the hard drive, system power supply, or CPU fan, does.
Daily usage and heat have an impact on a CPU’s lifespan. If not longer, a CPU should last for at least 7 to 10 years. However, the lifespan of a processor standing alone is a different matter. How long do CPU last, then? The quick answer is that a CPU will continue to function if you still find it useful.
What is the Lifespan of A CPU?
A CPU may readily operate for more than 10 years without breaking down. Most of the time, when a CPU malfunctions or dies, it’s due to a chip fault or a bent pin. Most computers’ motherboards will fail before their CPUs do.
Some users have had the same CPU in their computers for over ten years with no issues. Your CPU is good for the long term if treated properly and if it has lasted longer than a year. CPUs rarely change age as quickly as GPUs. Before starting to lag and experience performance concerns, a CPU can keep up with advancements for around 5 years.
Related Article: What are Motherboard Fan Connectors and How to Connect Them?
How Long Do CPUs Last for Gaming?
A CPU will last ten years for high or moderate frequency gaming. A CPU’s lifespan could reduce to five years if it is continuously used and overclocked for performance.
CPUs are not subject to the same demands as GPUs. It enables gamers to keep the same CPUs in their build for a long time. However, updating the CPU every five years will guarantee that your system can run the most recent games and that your CPU won’t wind up causing your GPU to bottleneck.
How Long Will CPU Last Without Fan?
How Long Do CPU Fans Last? The average fan lasts between 30,000 and 50,000 hours of continuous use, or 3.5 and 6 years. It does not imply that all supporters will last for the same period. For instance, a case fan might run for 5–6 years, whereas a laptop fan might survive for closer to 10 years.

You can operate a CPU without a heat sink for approximately a minute, but it will be warm and probably close to 80C. Since there is no other cooling available, the ambient room temperature will also have an impact. Please remember that I cannot guarantee that your CPU won’t harm by this.
How Long Do CPU Coolers Last?
Running your CPU without a cooler, even for a short while, is not advised. If the CPU is not adequately cooled, its heat will harm the processor. High-end CPUs on the market nowadays will last up to a few seconds with a cooling system.
Turning on your CPU without a heatsink and cooler is not advised. Low-cost CPUs needed to clock more quickly and produce less heat than their more expensive equivalents. These could be used without a cooler for a while without suffering harm.
Use a cooler even if you are testing your CPU because the danger is not worth the potential gain. If it becomes damaged, you could have to replace it entirely or figure out which component of the CPU has to be changed, such as parts with burnt markings.
Can You Use A CPU Used Without Coolers?
No, a CPU must have cooling to function. Without a cooler, a CPU will overheat and eventually stop working. A heatsink and fan are required because a CPU generates heat while it is functioning. The heatsink makes to dissipate that heat, and the fan circulates hot air away from the parts of your computer. At the same time, they also cool the heatsink.

How Long Do CPU Radiators Last?
All-in-one computers typically survive between 3 and 7 years if you take good care of them. Only 1-3 years allot for a personalized loop. However, you may increase that lifetime with proper maintenance and care.
The liquid then passes through the radiator’s halfway channels, where heat may draw from aluminum or copper fins. The fans disperse the radiator’s heat, which also cools the liquid. In the radiator, the liquid turns around and proceeds through the remaining channels.
Depending on the radiator, the pump wishes to endure 8 years or 70,000 hours. Depending on how frequently and for what purposes you use it. You might get more or less time out of the AIO on your computer because there are more individual pieces in custom loop systems than in AIOs.
They often last less time than AIOs. However, you can unquestionably increase the lifespan of the custom loop to rival that of an AIO with the proper care. Some people claim to live for up to 5 years.
How Long Do CPU Last Windows?
CPUs should be reliable for at least 8 years. According to CPU manufacturers, an average CPU predicts to endure 100,000 hours or more than 11 years of continuous use. CPUs seldom malfunction and have incredibly stable functionality.
However, specific subpar CPUs will malfunction after a brief period, but these concerns as dead-on-arrival failures rather than failures from use. Since CPUs are so functionally sound, their usability is a key factor in determining how long they will last.
As they age, CPUs become unusable and incompatible with newer technologies. When the CPU’s usage considers, the typical lifespan is between 3 and 5 years.
How Long lasting Are AMD CPUs?
It’s a relatively low estimate, but AMD’s engineers and developers rate their CPUs to have a shelf life of at least 5 years. However, this figure is most likely a significant understatement and does not accurately reflect performance in the actual world. Because AMD CPUs have a reputation for operating hotter than their Intel counterparts in recent years, keeping your AMD CPU cool will enable it to operate at its full potential.
When it comes to overclocking, the major distinction between AMD and Intel CPUs is that all AMD chips are unlocked, in contrast to Intel, which only offers specific variations of the same chip, some of which are locked. There are many safe methods for overvolting AMD processors, but exceeding their suggested voltage level may harm the chip.
For instance, the default voltage ratings of all current-generation Ryzen processors range from 1.3 to 1.4 volts. The predicted lifespan of an AMD chip can significantly reduce if these chips cross the recommended voltage, such as 1.5v or above.
How Do You Know If Your CPU is Dying?
Remember that the CPU might not be to blame even though you might be experiencing one or two of these symptoms. For instance, the computer failing to boot indicates a motherboard and CPU failure. Here are some warning signals of a dying or dead CPU:
1) Your Computer Abruptly Shuts Down
The experience of having your computer shut off suddenly cannot be pleasant. It could be a low battery problem when it first occurs. However, you should consider it a warning sign from your CPU if it keeps happening and does so at odd intervals.
Even though this occurrence may seem random, it typically occurs when the CPU overheats from overloading tasks. Without a solution, this will keep happening, and eventually, the CPU will stop functioning.
2) Frequently Overheats
An overheating computer is innocuous until the parts start to burn, and the device abruptly shuts down. If a broken fan is not to blame for your computer’s overheating, the stress load on the CPU is. And if it occurs even after light use, it can signal that the CPU is failing.
3) Freezing and Sluggish Reaction
When you are working on the computer, and it takes time to reply or freezes, the CPU is probably failing. It can occur both when you first turn on the computer and when it is not in use. The good news is that when you troubleshoot the computer, you can rapidly eliminate this effect.
4) Boot-up Issue
Your computer displays an error message after running the Power-on self-test each time you turn it on. This test may occasionally identify and describe a problem. However, the test may not always accurately identify and pinpoint the real issue, which could be a CPU on its last legs.
5) Your PC Won’t Boot Up
Your computer briefly turns on before shutting down without displaying anything. All of these could be symptoms of issues with different sections of the computer, including the CPU.
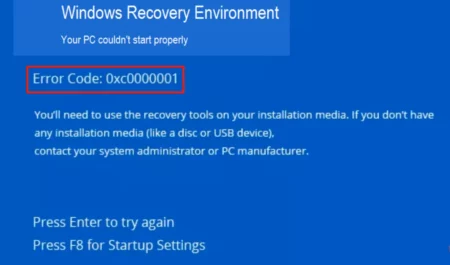
6) Computer Error
The term Blue Screen of Death exists. An error message explains why your computer crashed and cannot function. It was most likely given the nickname “Blue Screen of Death” because of its color and message.
CPUs make to operate securely at full CPU use. You should stay away from these circumstances, though, whenever they make games feel noticeably slower.
I can reconnect it to your motherboard without a problem. Unfortunately, replacing it is usually considerably easier and more cost-effective if it has failed.
If you are not running any extra programs, Windows processes should use between 1% and 10% of your CPU. Anything higher than that on an idle PC suggests a potential problem.